How to use mannure in organic farming?
Organic farming relies on natural methods of soil fertility management, and one of the main ways to achieve this is by using organic manure. Here are some steps to follow when using manure for organic farming:
Select the right type of manure: Different types of manure can vary in nutrient content and availability. Some of the common types of organic manure used in organic farming include cow dung, poultry litter, sheep and goat manure, and horse manure. You should choose the type of manure based on the nutrient requirements of your crops and the nutrient content of the manure.

Read more: How To Start Organic farming Business?
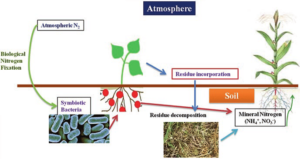
Compost the manure: Fresh manure can be high in nitrogen and other nutrients, but it can also contain pathogens and weed seeds that can harm your crops. To reduce the risk of disease and weed problems, it is best to compost the manure before using it. This can be done by piling the manure in a compost bin or pile and adding carbon-rich materials such as leaves, straw, or sawdust. The compost should be turned regularly to ensure even decomposition and good aeration.
Apply the manure to the soil: Once the manure is composted, it can be applied to the soil. The amount of manure to use will depend on the nutrient requirements of your crops and the nutrient content of the manure. A general rule of thumb is to apply 1-2 inches of compost to the soil surface and work it into the top 6-8 inches of soil. You can also apply the compost as a mulch around the base of your plants.
Use manure tea for foliar feeding: In addition to using composted manure as a soil amendment, you can also make manure tea to use as a foliar spray for your plants. To make manure tea, steep a bag of composted manure in a bucket of water for several days, then strain out the solids and use the liquid as a fertilizer for your plants.
Read more: Why Organic Fertilizer Is Important?
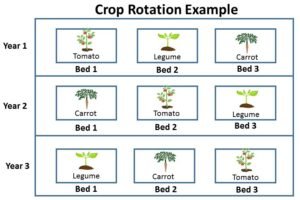
Rotate crops and use cover crops: To maintain soil health and fertility, it is important to rotate your crops and use cover crops. Crop rotation can help to prevent nutrient depletion and reduce the risk of disease and pest problems. Cover crops, such as legumes or grasses, can help to fix nitrogen in the soil and improve soil structure.

By following these steps, you can use manure effectively as an organic fertilizer for your crops, while also improving soil health and reducing the risk of environmental damage.
How much organic manure to add in soil for fulfilling?
The amount of organic manure needed to fulfill the nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) requirements of a crop depends on various factors, including the crop’s nutrient requirements, soil nutrient status, and the quality and quantity of organic manure used. In this response, I will provide some general guidelines on how to determine the amount of organic manure needed to fulfill the NPK requirements of a crop.
Read more: Complete Guide To Start Organic farming Business In India
Assess soil nutrient status:
Before applying organic manure, it’s essential to know the soil nutrient status. Soil tests can provide information on soil nutrient levels, pH, and other properties that can affect nutrient availability to plants. Soil testing is usually done by a soil testing laboratory, and the results can provide guidance on how much organic manure is needed to fulfill the NPK requirements of the crop.
Determine the crop’s nutrient requirements:
Different crops have different nutrient requirements, and it’s essential to know the specific nutrient needs of the crop being grown. Crop nutrient requirements can be obtained from agricultural extension services or other reliable sources. The nutrient requirements of a crop are usually expressed as the amount of NPK per hectare or per acre.

Estimate nutrient content of organic manure:
The nutrient content of organic manure can vary depending on the source and quality of the manure. Organic manure can be categorized as either animal manure or plant-based manure.
Read more: What are the Organic Fertilizers ?
Animal manure: The nutrient content of animal manure depends on the animal species, diet, and age. For example, the nutrient content of cow manure is typically lower than poultry manure. The average nutrient content of different types of animal manure is shown below:
Manure type N (%) P2O5 (%) K2O (%)
Cow 0.5-1 0.2-0.5 0.4-1.0
Horse 0.5-1 0.2-0.5 0.5-1.0
Poultry (chicken) 3-5 3-5 2-3
Pig 0.5-2 0.2-0.5 0.5-1.5
Plant-based manure: Plant-based manure includes compost, green manure, and crop residues. The nutrient content of plant-based manure depends on the type of plant material used and the degree of decomposition. The average nutrient content of some plant-based manure is shown below:
Manure type N (%) P2O5 (%) K2O (%)
Compost 1-3 1-3 1-2
Green manure 1-2 0.5-1.5 1-2
Crop residues 0.5-1 0.1-0.5 0.5-1
Read more: How To Start Organic Farming?
Calculate the amount of organic manure needed:
The amount of organic manure needed to fulfill the NPK requirements of a crop can be calculated using the following formula:
Amount of organic manure (kg/ha) = (Nutrient requirement – Soil nutrient content) x 100 / Nutrient content of organic manure
For example, let’s assume that we want to grow tomatoes, and the soil test indicates that the soil has low levels of NPK. The nutrient requirements of tomatoes are 120-180 kg N/ha, 60-90 kg P2O5/ha, and 180-240 kg K2O/ha. We plan to use poultry manure.
The yield difference between organic and inorganic farming can vary depending on several factors, including the crop type, soil fertility, weather conditions, and management practices. In general, organic farming methods tend to produce lower yields than conventional (inorganic) farming methods, especially in the short term. However, studies have shown that over the long term, organicfarming can produce yields that are comparable to or even higher than conventional farming, especially in areas with poor soil fertility or under drought conditions.
Read more: How To Take Organic Certification In India?
Here are some of the main factors that affect the yield difference between organic and inorganic farming:
Soil fertility:
Organic farming relies on natural processes to maintain soil fertility, such as crop rotation, green manure, and composting. Inorganic farming, on the other hand, uses synthetic fertilizers to provide the necessary nutrients to the soil. In general, organic farming methods tend to improve soil health over time, leading to higher yields in the long term. However, in the short term, organic farming may produce lower yields if the soil is severely depleted.
Pest and disease control:
Organic farming uses natural pest and disease control methods, such as crop rotation, beneficial insects, and cultural practices, while conventional farming relies on synthetic pesticides and herbicides. While synthetic pesticides can provide effective pest control, they can also harm beneficial insects and lead to the development of pesticide-resistant pests. Organic farming methods may be less effective in controlling pests and diseases in the short term but can lead to a more balanced ecosystem in the long term, resulting in fewer pest problems.

Read more: Difference Between Organic Farming & Sustainable Farming
Crop type:
The yield difference between organic and inorganic farming can vary depending on the crop type. Some crops, such as corn and soybeans, tend to have higher yields in conventional farming, while others, such as fruits and vegetables, can have comparable or higher yields in organic farming.
Weather conditions:
Weather conditions, such as rainfall and temperature, can affect crop yields in both organic and conventional farming. Organic farming methods, such as cover cropping and crop rotation, can help to improve soil moisture retention and reduce the impact of droughts, leading to higher yields in dry years.
Read more: Complete Guide For Organic Farming Of Vegetables
Overall, while organic farming methods may produce lower yields in the short term, they can lead to higher yields in the long term, especially in areas with poor soil fertility or under drought conditions. Additionally, organic farming methods have been shown to have several environmental and health benefits, such as reducing soil erosion, improving biodiversity, and reducing exposure to pesticides.